The complete guide on how to use SEO to increase your search rankings.
If you are the owner of a small local business, chances are you’ve been bombarded with emails and calls from businesses offering an SEO product or service. Even after removing yourself from mailing lists, and adding your phone number to do-not-call lists, the phone calls keep coming in.
Although you’re not interested in the sales pitches, you may be interested in SEO for your business. You just don’t trust your company’s website to these random agencies spamming your voicemail and inbox.
You don’t want to sign a long-term retainer with some company you haven’t even heard of.
Perhaps, you’ve paid for SEO before and never saw any return on your investment.
As a business owner, you are probably already familiar with the practice of bootstrapping (also known as “doing it yourself.”) You may be wondering if you could do SEO yourself.
The answer depends on who you ask.
A lot of people will probably tell you, “no.” Chances are, the same people who tell you that you can’t do SEO on your own are those who want to sell you on their services. They’ll offer you questions such as, “You wouldn’t change the motor in your car, would you?” They’ll follow that with, “Why wouldn’t you trust your SEO services to anyone but a professional?”
There’s a problem with that entire thought process.
Perhaps you would replace your car’s motor if you had the time, motivation, and skillset to do it properly.
SEO is no different!
Sure, it’s a complicated industry, with various right and wrong ways to do it. But, like with any skill, SEO can be learned by anyone with a little patience and time to dedicate to and invest in it.
So, if you’re looking to save money by doing your own search engine optimization for your business website, this guide for small business owners is the perfect place to start. (Check out our SEO Bootcamp afterwards if you really want to get indepth about SEO.)
We’re going to introduce you to the basics of SEO and educate you on what you need to know to help boost your business website in the rankings. (we’ll even introduce you to some more advanced SEO topics.)
Hang in there! Once you understand SEO for local businesses, you’ll be equipped to determine what tasks are worth doing yourself, and which ones you’d be better off outsourcing. So here we go!

SEO 101: Understanding the Basics
Going into this guide to SEO for business owners, we are going to assume that you know little to nothing about search engine optimization. That’s why, in this section, we will offer a basic overview of what SEO is and why it matters.
SEO is a Competition
Everyone has a competitive side, right? We like to think of SEO as a competition with other businesses that are trying to reach the same pool of customers as you. The object of the competition is better rankings in Google, Bing, and other major search engines.
The higher your page ranks, the more potential customers view your website.
The more people that view your website, the more sales leads you acquire.
The more leads you acquire, the more deals you close.
The problem is, that the bigger your audience, the bigger your competition. A global eCommerce website selling cleaning products will have to put in way more time and work to dominate search engines, than a mom and pop store with a physical location who services Tulsa alone.
Let us explain: Competition for local search rankings is relatively low compared to global search rankings. The odds are in your favor!
SEO for your small business is actually an attainable do-it-yourself-task. You can make good headway on your own, as long as you have a solid system to follow. (HINT: you’re reading one.)
The entire SEO competition revolves around two major ranking factors: on-page and off-page SEO. Both are equally important. Here’s a description of each.

What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO is basically everything on your website that you have complete control of that lets Google know what your website is, and what you should rank for.
For instance, when a guitar dealer in Oklahoma publishes a new service page about their new line of guitars for sale, they have to determine what content on that page they will create that will make it rank higher.
We’ll dive deeper into content generation later, but for right now, this illustration will help you understand the concept. Here are some things that the guitar dealer may do to strengthen his on-page SEO:
- Title the page “Guitars for Sale Oklahoma”
- Include phrases like this within the content of the page: “Oklahoma guitars for sale,” “buy guitars Oklahoma,” and “purchase guitar in Tulsa, OK”
- Add images to showcase the new products
- Create a contact form with an easily noticeable phone number and business address.
Because all of these items are implemented on the page itself, they are known as on-page SEO factors, and each on-page SEO factor helps the search engines better understand exactly what your page should rank for, and why it should rank over other pages.
What is Off-Page SEO?
We bet, you’ve already figured it out. Off-page SEO is the items that occur outside of your website. Typically, this refers to other sites linking to yours (that’s called backlinks).
For example, if that guitar dealer posts an article entitled, “10 ways to quickly change guitar strings,” and it gets shared by 100 people via Facebook, search engines will see that as a signal that the post is popular.
Off-page SEO is Google’s primary way to determine how authoritative and trustworthy your website is. Basically, the harder the backlinks are to acquire, the more powerful they will be in boosting your rankings.
For example, if a global guitar magazine picks up the guitar dealer’s article and decides to link it to a “tips and tricks,” article online, this link carries more weight (authority) than a Facebook share.
In the same way, a backlink could do more harm than good. So much so, that dangerous backlinks are referred to as “toxic.” If your website is getting high amounts of backlinks from spammy websites with low-quality content, your rankings could suffer. For this reason, a big part of effective off-page SEO is intentionally acquiring the right kind of backlinks and avoiding the wrong kind.
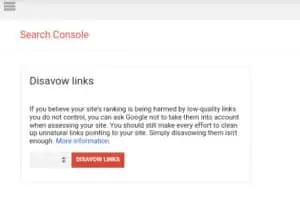
The good news, is Google understands that some toxic backlinks just happen, and have introduced the disavow tool, that allows you to notify them, and have them not count against you. (We’ll go into more detail in a later post.)
Keyword Research for Small Businesses
Remember previously how we said that SEO is a competition? Well, let’s take it a step further. It’s like running dozens of races at the same time!
In SEO, each race targets a separate keyword. A keyword is a search term that users enter into the search engine.
For example, a car dealership serving the Tulsa area will be running a race to page 1 for each of these keywords:
Cars for sale Tulsa, pickup truck Tulsa, Tulsa car dealership, SUV Tulsa, etc.
Each race is separate. The dealership could rank on page 1 for “cars for sale Tulsa,” but not even rank for “SUV for sale in Tulsa.”
That’s why the first step in your business SEO process should be determining what keywords you want to rank for, and create content accordingly.
This process is called keyword research. While volumes of books have been written on how to do keyword research, we’ll just give you an overview on how to do keyword research for your local business here.
Step 1: Get Search Volume
The first step in keyword research is to figure out what people are searching for. Keywords Everywhere is a tool that SEO professionals used to recommend to novices. It was a good tool for most business owners because it was simple and free. Unfortunately, it now comes with a price tag.
Personally, when Keywords Everywhere became paid on Oct 1, I uninstalled the extension immediately. Not because I can’t pay. But rather, to get myself to go out there looking for something new and even better. (we use a professional analytics stack of Ahrefs and SEMRush)
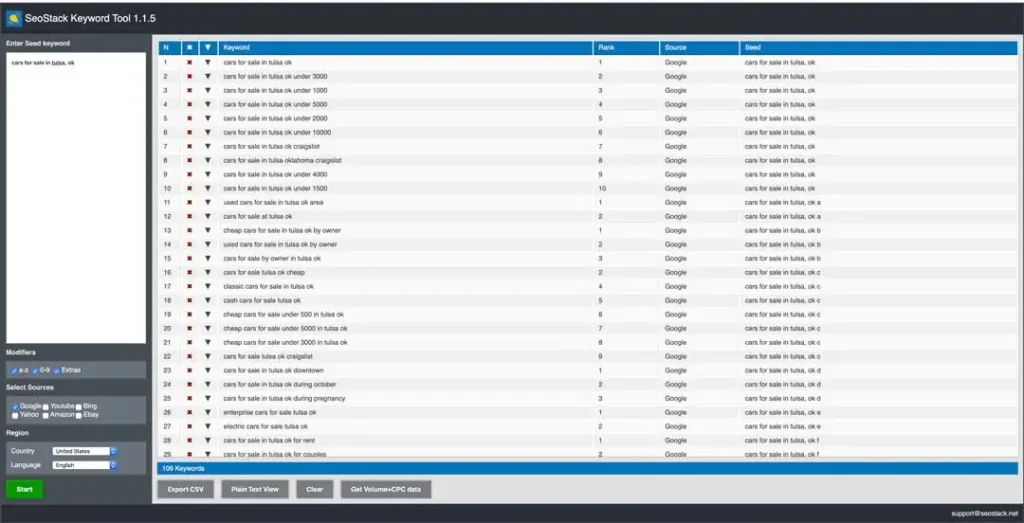
SEOStack is a free chrome extension and from our point of view is the best alternative tool of Keywords Everywhere. It can be used to easily generate a long list of keywords.
How to Use
- Just install the extension from download the extension.
- After complete, the installation clicks on the SEOStack tool and you will get a window like the image above.
- Just type the keyword in the “Enter seed keyword” field and click on the Start button.
- You will get the related keywords.
- You can select sources from YouTube, Bing, Yahoo, Amazon, and eBay in addition to Google.
Pros
- Generate a list of long-tail keywords quickly and easily
- Easy to use
- Multiple tabs to get multiple results
- Country and language filters options
- Suggestions from Google, YouTube, Bing, Amazon, Yahoo, and eBay
- Easy export CSV
- Get volume and CPC data (requires a Google Adwords account)
Cons
- Need Google Keyword Planner to extract CPC metrics
- Only for Google Chrome
Pricing
- Free
Step 2: Find Your Service Keywords
Now that we have a general list of keywords, we want to find all of the variations of them for your services, industry, and location. SEOStack will help you determine, for instance, if more people are searching for “roofing contractor in Tulsa” or “Tulsa roofer”.
Be sure to keep a spreadsheet or list of each keyword and their monthly search volume. Then narrow down the list for each service to those with the highest search volume.
Step 3: Find Your Long Tail Keywords
Some consider this to be an optional step, but not us. Long-tail keywords are where you make your money!
Long-tail keywords are key phrases that are more specific – and usually longer – than more commonly searched for keywords. Long-tail keywords get less search traffic, but will usually have a higher conversion value, as they are more specific. They allow you gradually to get more traffic and to be found by new and motivated audiences.
For example, perhaps you are a personal trainer who wants to help customers lose weight. Sure you could optimize your post around the keywords “lose weight,” but it would be difficult to rank high for that phrase.
Let’s just say you use the Keto diet to help your clients. Well just pop those extra words in your keyword phrase. Now you have, “lose weight keto diet,” or if you want to get extra-long, “trainer who uses the keto diet.”
On-Page SEO for Business Owners
Now that you’re armed with a good list of keywords to target, it’s time to start creating quality content, whether for a new site or optimizing existing content.
Optimizing on-page SEO for business owners typically involves making minor (and major) changes to the content and structure of your posts and pages.
These changes are intended to improve user experience for visitors and give search engines a better idea of what your site’s content is all about.
Site and Content Structure
These are the basic steps that you should take to ensure that your site and its individual pages are best optimized for your target keywords.
Create One Page Per Keyword
Every keyword that you are targeting should have its own page or post. A good rule of thumb is to use pages for product-oriented keywords, and posts for long-tail keywords.
Don’t target the same keyword on multiple pages. This is what’s known as keyword cannibalization, meaning that your pages are competing with each other for rankings.
Similarly, don’t create separate pages for similar keywords. “Tulsa radio station” and “radio station Tulsa” don’t need separate pages (you could also get snubbed by Google for having duplicate content).
Optimize Each Page for Your Keyword
The SEO community and industry has best practices that give the search engines a little help in knowing what your page is all about. Remember, the search engines’ goal is to answer the user’s query (search) by providing the most relevant information to the question asked.
While not always a question that ends with a question mark, as far as search engines are concerned, when you hit that search icon in the box, you are asking a question.
Here are some best practices for letting search engines know how you can help answer the question:
- Put the keyword in the URL (use a hyphen to separate the words).
- Include the keyword in the page title and <h1> tag (heading 1)
- Include the keyword in the meta description (NOTE: this doesn’t directly impact search engine results, but does help increase click-through rates).
- Use your keyword in the text naturally, don’t overdo it! (NO KEYWORD STUFFING!)
Structure your Service Area Pages
One trick to help you succeed in your local SEO efforts is to develop a separate landing page for each of the major service areas that you do business in.
For example, if you are a painter in Tulsa, Oklahoma, naturally, your home page is going to target “Tulsa painter” as the main keyword. However, you can expand your geo-relevancy by creating a subpage for suburbs like, “Owasso painter,” “Walker painter,” or “painter in Sand Springs, Oklahoma”
Ideally, each of those pages should have geo-specific content on it. Mention local landmarks or major business entities present in the areas. Although it may seem silly to do this, Google will recognize that your website is a hub or relevancy for your area and industry.
Create Natural Internal Links
Internal linking is one part of on-page SEO that business owners often overlook.
Internal linking is simply connecting one of your pages to another via hyperlinks. This small process packs a big punch in helping boost your rankings. Every link that you build on your page not only helps the search engines better understand your content, but they also help the crawlers navigate your website as a whole.

What is a Crawler?
“A Web crawler is sometimes called a spider or spider bot and often shortened to crawler, is an Internet bot that systematically browses the World Wide Web, typically for the purpose of Web indexing (web spidering).
Web search engines and some other sites use Web crawling or spidering software to update their web content or indices of other sites’ web content. Web crawlers copy pages for processing by a search engine which indexes the downloaded pages so users can search more efficiently.” – Wikipedia
You can this and other SEO terms defined in our Urban SEO Dictionary.
Not having internal links on your pages is akin to sending the spider down a dead-end road. Keep traffic flowing by using the following tips:
- A good rule of thumb is, for every page, link to four other pages.
- Place the links naturally in ways that help users navigate your site.
- Use your keyword or variations of your keyword for your anchor text (the visible text portion of a link), but don’t force it!
- Please don’t ever use click here, give the user an indication of what they’re clicking. We try to use a verb, for example, “read suggested articles.”
Best Practices for Landing Pages
Sure, these tips involve making sure that search engines “like” your website, but you must make sure that you create pages that your users will love! Create landing pages for users, not just search engines!
A major part of Google’s algorithm involves how users react to your website. Remember, Google wants to provide the best results for the user’s search. If a user leaves your site after only a few seconds, chances are, they didn’t find what they were looking for and “bounced” back to the search results. High bounce rates will cause your rankings to suffer!
Avoid high bounce rates by properly designing your pages. A lot of traffic is of no use if the visitors don’t convert into customers. Here are a few things that you should focus on to design pages for both SEO and conversions:
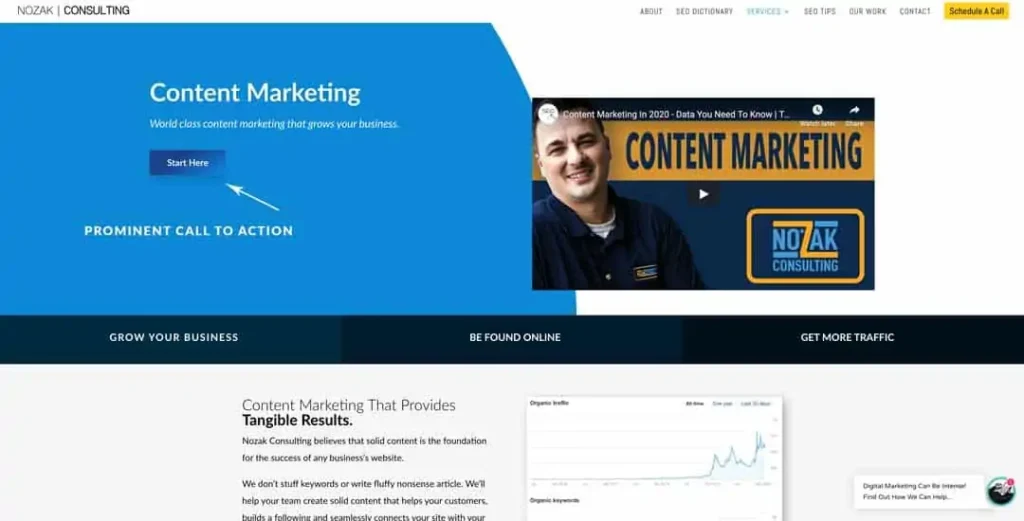
Include a CTA (Call to Action) Above the Fold
The whole goal of your landing page is to convince customers to contact you right? Well, they can’t do so without knowing how to do it.
This can easily be done by using a call to action (or CTA). A CTA is typically a button with a phone number, a contact form, or a way to sign up for your newsletter for example. (the above image from our content marketing page is a perfect example).
Your CTA should be placed “above the fold,” meaning that the user sees it in their viewport (screen) before having to scroll down the page.
You can have multiple calls to action throughout the page, but make you definitely want one to be the first thing users see when they land on your site.
Arrange your content in chunks
We don’t read websites, we scan them.
Should your user not click your CTA and continue to scroll down your page, you want to make their reading experience as smooth as possible. If you present them with one group of text that’s difficult to read, chances are, they’ll bounce right back to the search results to find someone else.
Instead, break your content into bite-sized pieces that are easy to read and scan. Here are some easy ways to chunk your content:
- Use big bold headings to divide your content into sections
- Write content in short paragraphs of about 1-3 sentences (you don’t have to follow your 4th grade English teacher’s rules here).
- Break up sections of text with images.
Add Social Proof
You need your users to trust you if you want to keep them on your page. If they trust you, they’ll be more likely to stay on your page and not go look elsewhere for services.
Social proof is a marketing strategy that you can use to build trust in your brand, simply because others do too. This is the bandwagon effect applied to marketing. Here are some simple ways to add social proof to your landing pages to build trust and increase user engagement:
- Add customer service reviews or testimonials
- Include local press or publicity you’ve received
- Share statistics about your customer base and clients
Optimize Page Speed
If your page loads slowly, people aren’t likely to stick around. With more people surfing the web on their mobile devices, it’s critical that your website loads fast. Users expect fast websites!
Consider this: Every second in added page load time decreases conversions by an average of 7%. Don’t lose potential sales for your small business! Here are some of the most important steps you can take to optimize your page’s speed:
Check Your Current Page Load Speed
We like to use GTmetrix to see just how our pages are loading, and what we can do to speed them up. Simply visit the website, plugin your domain, and get an overview of where your page speed stands currently.
After analyzing your page’s load speed, GTmetrix shows recommendations about what you can do to increase your site’s performance.
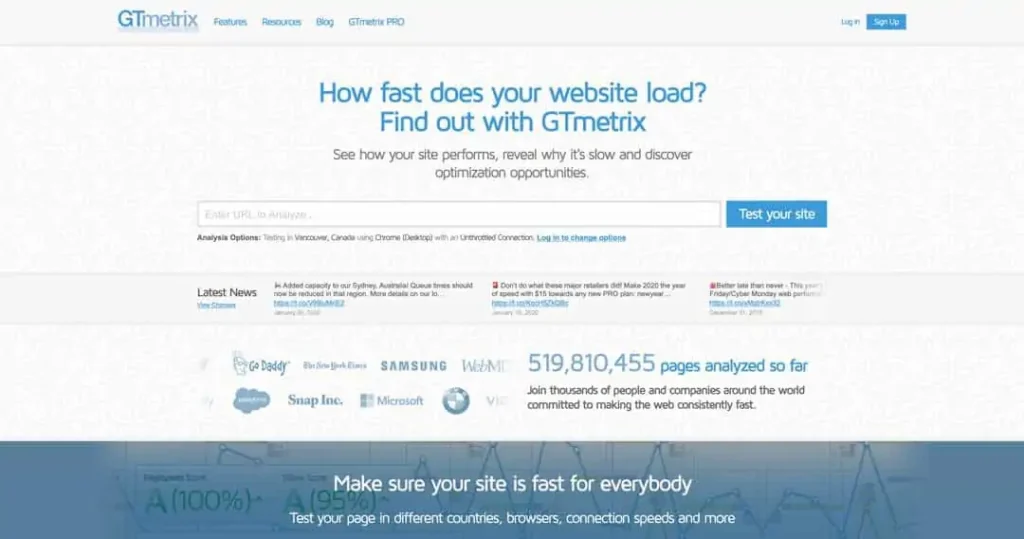
GTmetrix is one of the first things we do when performing an SEO audit, and we use the pagespeed score that it gives to create benchmarks for the site’s performance.
Install a caching plugin
We won’t bore you with all of the technical details. Caching is basically a method of storing data on your website so that it will load faster for returning visitors. If your site is built on WordPress, we highly recommend the WP Rocket plugin (we use it on all of our sites).
Although not free, it’s well worth the price, and set up is so simple, even the least technically savvy business owner can do it!
Optimize images
Large image files are one of the biggest causes of website bloat. It’s quite possible that you are serving images at sizes 10 times larger than are actually required.
Serve large images multiple times across the same page, and you have slowed your page (or site) down to a crawl. Luckily there are ways to prevent this.
Typically, we optimize our images manually. We determine the actual size of the image needed and then crop them accordingly in Adobe Photoshop. Sure, this takes more time, but the end result of a faster website is worth it.
Next, we use a plugin called Imagify to bulk compress the images, decreasing the image’s file size and load time. It’s easy to use, and the free version allows for compression of 25mb per month.
There is no on-page SEO recipe for success
Although we’ve discussed the most important aspects of on-page SEO, it’s important to realize that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Google’s algorithm changes almost daily, and its ranking factors seem to change with change twice as fast.
It has even been said that Google has a separate set of ranking factors per keyword. This means that while page speed will always be a factor, something like keyword density may not factor as heavily for one niche as the next.
But, you don’t have to recreate the wheel. Remember the old joke about outrunning a lion? You don’t have to be the fastest, just faster than someone else.
In small business SEO, this means that you want to see what your competitors are doing, and just do a little better.
Although there are free options available, we prefer to use our premium SaSS Cocktail of Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, SEMRush, Google Search Console, and Google Analytics (for starters).
Off-page SEO for business owners
Now that you have your on-page SEO taken care of and dialed-in, it’s time that you start working on your off-page SEO.
To review, off-page SEO factors are those signals that Google picks up outside of your website that help prove your relevancy and authority. Whenever a website links back to yours, or someone shares your content on social media, that’s off-page SEO.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to developing solid off-page SEO for business owners:
Anchor Text in detail
Before you start building your backlinks, it’s important that you understand anchor text. Anchor text is the text that makes up the portion of a link that your users see. For example, the following link uses the text, “SEO Consulting in Tulsa” to point to the URL https://blaksheepcreative.com/services/affordable-seo-services-for-small-business/
Anchor text is extremely important when building your backlinks.
There are numerous types of anchor text to keep in mind. We can show you better than we can tell you, so let us demonstrate.
Our business is called Nozak Consulting, right? Our website (obviously) is https://nozakconsulting.com right?
In this example, let’s just say we are trying to rank for the keyword “Best SEO Agency in Oklahoma” Here are some of the various types of anchor texts that could be used:
Exact Match: Uses the word-for-word keyword that the target page is trying to rank for. So, the link would look something like this: Best SEO agency in Oklahoma
Partial Match: Uses a variation of the keyword as its anchor text: SEO Tulsa, OK
Branded Anchors: Use the business or brand name: Nozak Consulting
Generic Anchors: Use unrelated text: Click Here (we hate that remember?)
Naked Anchor Text: Uses just the URL: https://nozakconsulting.com/seo-consulting/
This is important because, as you begin to build your small business backlinks, you want to keep a natural ratio of the different types of anchor texts.
More importantly, you want to keep your exact match and partial match anchors low in relation to the other types. If all of your links have your keywords as anchor text, Google will view this as an unnatural link building strategy, and possibly, penalize your ranking.
Now let’s look at the steps of off-page SEO for local businesses:
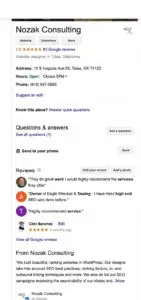
Step 1: Create your Google My Business Page
If you’re a local business owner, you’ll definitely want to rank in the Google Map Pack, the list of local businesses that appear at the top of the search results page when people are searching for local services.
This is prime real estate for the search engine results pages and where the battle for local SEO is won.
The Google Map Pack is a major source of leads for local small businesses, so it stands to reason that one of your first SEO strategies should be to create a Google My Business page to rank in the maps. Fortunately, this process is pretty simple:
- Just head over to https://www.google.com/business and create a new profile (or sign in if you already have one).
- Fill out as much information about your business as possible, making sure that your business name, address, and phone number are all correct.
- Google requires you to verify your address and will send you a physical postcard with a code that you’ll have to enter on your GMB profile. Your listing will NOT be live without being verified, so make sure you do this step. Follow up with Google if you don’t receive one.
Check our complete guide to Using Google My Business for more info about GMB.
Step 2: Acquire Business Citations
Business citations are perhaps the most important factor in getting your website ranked locally in the Google Map Pack.
If your business has been open for a while, chances are you have already built some of these citations, not even realizing they’re good for SEO.
For example, if your small business has a listing on Yelp, HomeAdvisor, Better Business Bureau, or the Yellow Pages, then you’ve got business citations.
Don’t stop there. There are hundreds of citations that your business can acquire, with each one giving you a small bit of online presence. These small bits signal to Google that you’re a legitimate company that should be noticed and ranked.
Here’s a small list of the major places to get citations. There are literally hundreds that we can provide for you, just get in touch with us for more info.
- Yahoo Local
- Hot Frog
- Bing Places
- BizJournals
- Better Business Bureau
- Yelp
- Foursquare
- Angieslist
- Manta
- HomeAdvisor
- Thumb Tack
It’s important when you are acquiring your citations that you fill out as much information as you can. Add your logo, business name, images, and business description (if available). Basically, if they provide a blank, fill it out!
Make sure to keep your name, address, and phone number (often referred to as NAP) consistent. Everywhere that your business has an online presence should use the same business name, address, and phone number. If there are any variations, no matter how minor they are, your rankings will take a hit.
Step 3: Build foundation links
Foundation links are backlinks that are used to establish the presence of your small business online. Although these links are relatively low power, they are still important. They add legitimacy to other links that you will acquire later on and help Google see you as an expert in your niche.
Additionally, foundational links are a great way to diversify your anchor text ratio. For these links, you’ll want to incorporate branded, generic, and naked anchors.
Ultimately, you’ll create hundreds of foundational links, so they’ll give you ample room for using exact and partial match anchor texts on your more powerful links later on.
Here are a few different types of foundational links that you should acquire:

Social Accounts
Any legitimate small business is going to have some sort of presence on social media. That’s why creating these accounts is necessary. We tell our clients if it allows you to create an account, create one. Leverage every social media network possible, even MySpace.
In a perfect world, you would keep them all updated with content, but that’s not worth losing any sleep over. Simply having an account is sometimes good enough.
Here are some basic social accounts that you should acquire:
- Facebook Page
- Facebook Group
- YouTube
If at all possible, create these accounts with your brand name in the URL. BlakSheep Creative, for example, would aim to acquire https://www.facebook.com/blaksheepcreative. This helps build keyword relevance for your brand name. (sidebar – that’s our Facebook page link).
Profile Links
Profile links typically involve creating a presence for your business or brand on community websites. One such example is Goodreads.
While Goodreads might not be the best location to reach your target audience, websites such as this allow you to build out a profile that includes a backlink to your website. Whether or not the backlink if a follow or no follow link remains to be seen, but we’ll discuss that in another post.
What’s important is to find some community sites that fit your niche (or industry), and fill them out. Here are some examples:
- zotero.org
- stationfm.ning.com
- smashwords.com
- shapeways.com
- mobypicture.com
- kickstarter.com
- issuu.com
- intensedebate.com
- ifixit.com
- goodreads.com
Web 2.0s
A Web 2.0 is typically a blog or a microblog where users generate content about a specific topic or niche.
Building links from Web 2.0s helps establish your company’s authority and relevance in your industry. This can easily be done by creating a new account on various Web 2.0 sites, writing articles that demonstrate your expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. This is commonly referred to as Google as E-A-T.
When you post this content, include a link back to your business website (the most natural way possible – most just add it in their signature line). Here’s a list of some websites you can start with:
- wordpress.com
- tumblr.com
- disqus.com
- goodreads.com
- bravenet.com
- livejournal.com
- evernote.com
- liveinternet.ru
- webs.com
- over-blog.com
Social Signals
When someone shares your content on Facebook or pins on Pinterest, this is known as a social signal. Social signals are crucial in SEO efforts in 2023 because they demonstrate to Google and other search engines that your business is relevant to your audience.
While social signals don’t directly boost your rankings, they do add a sense of legitimacy to your other backlinks and are a necessary part of the rankings formula.
Getting social signals is still a bit of a challenge these days.
Similar to SEO, there are two core elements of social media: onsite and offsite. In order to properly establish and grow a social media campaign, both elements must be present and refined.
Onsite elements include:
- Share buttons (like, recommend, tweet, bookmark, etc.)
- Connect buttons (Like a Facebook page, Follow on Twitter, Follow on LinkedIn)
- A blog
Offsite elements include:
- Facebook page
- Twitter account
- LinkedIn company page
- Pinterest account
- Youtube account
- Guest blog posting
- Other social media platforms
Create share-worthy content (sometimes called share bait), and the rest will come naturally.
Step 4: Wait, Wait, Wait
If you’re like us, you don’t have patience. That’s why the most frustrating part of the SEO process is waiting.
SEO doesn’t happen overnight, so, after you’ve built all of your citations and foundation links, let them sink in. Give it a few weeks for Google’s bots to crawl the internet and to pick up on all of your changes (both on-page and off-page).
After a few weeks, see how your rankings adjust, determine what pages need tweaking, tweak, and wait some more.
Step 5: Acquire Authority Links
Once the dust has settled and you’ve made your first round of tweaks, it’s a good idea to start building more powerful links.
These higher authority links typically come from highly-relevant, very-trusted websites, and typically will consist of your exact or partial match anchor text.
Because these links are more difficult to acquire, they are more valued by Google as a ranking factor. Here’s a common source of authority links:
Guest Posts
To put it simply, a guest post is essentially an article published on an existing blog (with real traffic), that includes a link back to your website. They can be acquired by manual outreach, in which you email blog authors in your industry or niche and request to submit a guest post.
This method can be time-consuming but can pay great dividends if successful. As with anything else, you could always pay one of the hundreds of services that already have established, long-term relationships with bloggers to do the hard work for you.
Link Building Best Practices
The last topic in this article is viewed by some SEO professionals as one of the most important. Here are some important points about link building that you should keep in mind:
Send your links to different pages
Wondering where those guest posts should point to? Although you may be tempted to link to your home page, don’t always do it!
Linking to ONLY your homepage appears very unnatural. Think about it, it gives search engines the impression that only one page on your entire website is relevant.
Mix it up!
A good rule of thumb is to include one link to an inner page or post for every 2 links to your home page.
Diversify that anchor text!
Don’t stuff your authority backlinks with the same keyword over and over. Use close variations for each link. Some would go as far as to say, never repeat the same keyword-based anchor text.
Wait!
There’s that word again. Yuck.
Don’t just bang out a zillion links to your site all at once. After you build a few links, wait a few weeks for them to take effect. See how your rankings have improved, and then build more if necessary.
Don’t Panic!
Sometimes building a backlink will actually cause your ranking to drop temporarily. Don’t panic!
This is commonly referred to as the “Google Dance.”
What’s happening is Google is reassessing the authority of your site, but the good news (if you’re building quality links) is that you’ll come out ranking higher than before.
Now, put these SEO principles to use
This guide for SEO for small business equips you with all of the knowledge that you need to perform your own search engine optimization.
These are the exact same strategies used by us and SEO professionals across the globe.
If you apply these strategies, you WILL see your rankings increase.
We realize, however, that this is a lot of information to digest. If you’d like for us to come alongside you and help you with your SEO campaigns, or simply help you perform some keyword research, we’re here to help.
Just send us a message, and we can chat about your goals, and how to smash them.
