WARNING: Duplicate content doesn’t cause your site to be penalized!!
- Googlers know that users want diversity in the search results and not the same article over and over, so they choose to consolidate and show only one version.
- Google actually designed algorithms to prevent duplicate content from affecting webmasters. These algorithms group the various versions into a cluster, the “best” URL in the cluster is displayed, and they actually consolidate various signals (such as links) from pages within that cluster to the one being shown. They even went as far as saying, “If you don’t want to worry about sorting through duplication on your site, you can let us worry about it instead.”
- Duplicate content is not grounds for action unless its intent is to manipulate search results.
- About the worst thing that can happen from this filtering is that a less desirable version of the page will be shown in search results.
- Google tries to determine the original source of the content and display that one.
- If someone is duplicating your content without permission, you can request to have it removed by filing a request under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act.
- Do not block access to duplicate content. If they can’t crawl all the versions, they can’t consolidate the signals. (these bullets borrowed from Searchengineland).
What Counts as Duplicate Content?
If content appears in any location on the internet more than once, it is classified as duplicate content.
If the content is replicated across a single website or on more than one URL, it is classified as duplicate content. Even within a single website there can be duplicate content that leads to reduced SERP positioning for important content.
We don’t want to use the word penalty, but in reality, if you are duplicating your own content across multiple pages, it in the end will force Google to place certain pages in the SERPs and leave out others. Penalty? Not exactly, but it sure feels like one.
The easy fix is to modify the content on subsequent pages, so it is page specific and tagged as original. There are a lot of duplicate content myths out there, make sure you know what AHREFS said about it and what Moz says about duplicate content.
Remember, duplicate content isn’t just when copy is scraped from another website, it is also copy that is located on your own website on multiple URLs.
Both of types of duplicate content can negatively impact the SEO of a website, and while it is relatively easy to fix, there are many people who are not aware of the impact of duplicate content.
Googles definition of duplicate content is quite clear, and for many looking for ways to improve the SEO of their website, it is the ideal place to use as a reference point. Often times, fixing duplicate titles, H2s, copy, and metas can lead to quick SEO gains.
Defining Duplicate content – is substantive areas of content that are appreciably similar or a direct match to other content that is contained within a single domain or published across multiple domains. It’s not a huge deal if you are the author and secondly, but more importantly, you have the strongest website! The situation gets murkier if someone is outranking you for YOUR content, or vice versa.
There are ways to report this to Google. Side note, do you need to look up the online marketing terms we are using in this article?
Duplicate Content Examples
These are all examples of duplicate content that are not considered to be malicious in intent.
- Print-Only versions of website pages
- Pages that are not indexed by search engines
- Forums for discussion which generate pages that are web and mobile optimized
- Items within a store that are presented with a multitude of distinctive URLs (assuming rel canonicals are set up correctly)
- Pages that rel canonical to the original content
- Menus, footer sections, some sidebars, and other content areas not in the main “unique content” area of the website
- Content that has enough Geo-modifiers, modified H1s, H2s, and copy – even when it is pulled from a single set of files
- HTTP and HTTPS
- www and non-www
- Parameters and faceted navigation
- Session IDs
- Trailing slashes
- Alternate page versions such as m. or AMP pages or print
- Pagination
- Country/language versions
If your website has different pages where the content is mostly the same, there are lots of ways you can inform Google of your preferred URL. This is also typically referred to as Canonicalization.
Content that is copied from its author and pasted into a website or blog can also be referred to as plagiarized content. In this situation, the person copying the content makes it appear as their original content. A scraped blog or block of content rarely falls into this category.
Usually Google can figure out who the author is, a scraper isn’t typically trying to be an imposter, they usually just trying to offer information to their users. Once again, the issue comes when the scraped material outranks the original material.
To be safe, just add a link to the original or if it is an entire scrape of an others material, just rel canonical the post to the original source. Typically privileges are very easy to get, unless it is content that gives one website a competitive advantage over another. Even still this information is more often than not, usable with credit.
When a web developer scrapes content and places it on another domain, in order to steal the works of another company, this can in extreme cases, lead to penalties and the complete removal from the search engines.
Practices like this can destroy the user experience and is malicious, it is for this reasons that penalties are put in place by Google in order to both protect the user experience and penalize anyone who tries to use foul practice for gaining traffic or boosting their websites SEO.
Proper attribution must be used when information is borrowed from other online sources. Typically in a situation where someone is plagiarizing your website and posing as you, this is not something attribution is given to, because the author is committing an infringement that when caught will lead to a penalty.
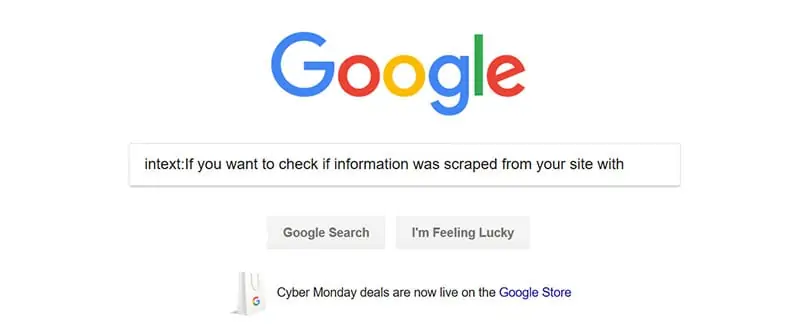
Google Advanced Search Operator to Find Duplicate Content
If you want to check if information was scraped from your site with no attribution just use a simple Google operator such as intext: and include a chunk of content you are curious about.
Additional google search operators that can help you find duplicate content scraped from your site include: intitle:, allintitle:, inurl:, allinurl:, allintext:. But honestly, most people don’t worry about this – most huge blogs are ripped continuously.
The trick to gaining something from this tactic is to include a solid inbound linking structure, that way you might gain some traffic or authority from these situations.
Is Duplicate Content Bad?
Yes? No? Maybe. It really depends on the situation. Google is pretty open about there being no real penalty for duplicate content as the internet is about 30% duplicate.
What would they do, just delete 30% of the content in their servers? How would they choose?
Almost 30% of online content is duplicate content. In malicious cases, It can cause confusion with the search engines as they do not know which version of the content should be ranked (depending on authority).
If we are being honest, duplicate content across multiple sites usually involves data-theft, where someone, even if it was done innocently, has stolen or copied content from another website or source.
There are many copyright laws and tools that can be used to detect plagiarized content. Remember, plagiarism is much worse than a simple scrape or even repurposed content on another website.
Not only does infringement include written word, but it also applies to other forms of media such as image and video content. There are lots of places to get free content to use, but most places cost and/or require attribution.
If you have copied content or duplicate content on your website, this can result in a number of key issues.
Not only is it considered to be lazy in today’s inter-webs, but in some cases, can portray an unprofessional or unethical image of your company, or your client’s company! Even worse.
Would you buy products of a business who knowingly steals and copies the work of others?
I know the answer is yes, right? The phone companies seem to be ripping each other off daily. But for a second, think about it in regard to online content.
If you hope to be the next content authority, duplicate content is not the way to go. We are not saying run from syndicating others original content on your website, we are saying, use proper attribution when you do so. Stay above board, when it comes to hosting others material on your URL.
Where is the line with Google? In extreme scraping/plagiarism, Google and other search engines could levy a manual penalty against your URL, damaging the profitability of your company from organic search traffic.
The purpose of any website is to attract and inform. When you have duplicate content on your website, you lose out in a huge opportunity to attract traffic to your website – especially when the search engine isn’t displaying your /url with the content. It’s really a risk with little benefit.
In summary, Duplicate content can be bad for your website and bad for your online efforts.
If you want to improve your SEO, then you can start off by updating your website content and making sure that any duplicate content is removed and replaced with original and engaging copy that is both relevant for your audience and unique to your business.
What is Thin Content?
While the aim of this article is talking about ways to detect duplicate content, it seems appropriate to quickly cover another category of content that is considered to be bad for SEO.
Since, thin content can be caused by containing duplicate content. Learn more about good blogging from Yoast and how to avoid thin content.
Since the original introduction of Google Panda and the subsequent updates to how Google ranks a website; there has been a concurrent theme of penalizing website that have low-quality content.
Thin Content is content that delivers none to little value to a visitor. It can be further defined as low-quality pages on a website or within an eCommerce store.
Examples of Thin Content include automatically generated content, duplicate pages, and doorway pages.
If you have a page on your website that users don’t stay on for too long or one which is clearly bouncing people away from your site, it is sometimes an indicator to the spiders that a page contains thin content.
Quite simply, if a page offers no value to a visitor and is bouncing people away from your site, there are issues with your content that you will want to address, quickly.
How Does Google Measure Thin Content?
Much of what Google measures is automated. When it comes to measuring thin-content, there is one particular metric that Google uses.
‘Time to Long Click’ is effectively when a person clicks on a result on a Google Search Page and then remains on the target site for some time.
Let’s say, for instance; you find an article you like, you might then want to have a look around the site for more useful information.
Then, let’s say you click on a link that is not useful, meaning you return to Google much more quickly to look for another site that provides either more comprehensive or more useful data. The latter is referred to as short click.
In order to make sure you are not penalized for having thin content, use the following pointers:
- Try to avoid using duplicate content on your site
- Try to make sure you provide information that is relevant to your customers or potential customers
- Make sure your page titles and descriptions match what is actually present on a webpage
- Try to ensure you have a minimum of at least 350 words per page
- Make sure that your content addresses any questions that a visitor might have
9 Tools for Detecting Duplicate Content

1. Siteliner
Siteliner is listed as number one on our list because it will check for duplicate content within a site, and it tells you exactly what text is replicated on what page.
It also checks for plagiarized content across the web and a whole lot more. It is very easy to use; you simply paste the URL for the site you wish to review and hit search.
On top of this, it also tells you other information such as the loading time for each page, the number of words present on each page, broken links, redirects, and more.
The speed of the scan depends on the size of the site you are searching, and results are presented at most, within just a few minutes.
Siteliner allows you to check areas that might contain thin content or content that is found on multiple URLs within your website, it also allows you to see the strongest pages.
It has an algorithm that compares all the pages of the site, taking into consideration IBLs, and shows you which pages are the strongest.
Once the report is produced, you can then email or download a copy of the full report for free. The freemium version of Siteliner is restricted to one scan of an individual site per month.
However, if you need to do more, the pricing for the premium service is extremely reasonable. You need to add a minimum of $10 credit, and then a minimal charge is made per page that is scanned, charged at just 1c per page.
Siteliner is brought to you from the same company that operated the Copyscape website.
2. Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog crawls a website in the same way that Google would. It allows users to detect a variety of issues with duplicate content along with a number of other useful features such as parameter issues with URLs and more.
We use Screaming Frog Premium to check for the following technical SEO issues:
- Protocol issues: http/https
- Response Codes: 4xxs, 5xxs
- URI: We check for standardization of our style
- Page Titles: missing, duplicate, length, multiples
- Meta Descriptions: missing, duplicate, length, multiples
- Meta Keywords: deprecated
- H1s: missing, duplicate, length, multiples
- H2s: missing, duplicate, length, multiples
- Images: size, alt text, alt text length
- Canonicals: Make sure our canonicals are set
There is a lot of functionality built into each of these sections and many other functions we don’t use regularly.
While they do offer a paid service, it is also possible to use a free version of their product that will scan up to 500 URIs.
Once you figure out which version you need, download the software to your computer. Side note, the free version provides enough ‘credits’ to scan the vast majority of sites.
3. Plagspotter
Hailed as one of the biggest rivals to the popular Copyscape plagiarism checker, Plagspotter is increasing in popularity, and with good reason.
It is a content detection tool that was developed by a company called Devellar. Using Plagspotter is simple, and just like many others in the same space, they offer both paid and free versions.
You simply enter the URL of the website you need to check, and the content is then analyzed. For a one-time search, there is no charge and no limitation in terms of the volume of results that are returned.
Copyscape, who are the nearest competitor limit free results to just ten, so in this aspect, Plagspotter outperforms by a long shot. In terms of the speed of the results, it falls short compared to many other plagiarism checkers that are available.
If you have a large site to crawl, this might not be the best tool to use right now. With that said, its user interface is bright, and the design is friendly and easy to navigate. There is certainly a hopeful future as this is a fairly new product to market and there are many new features promised in the development pipeline.
The only significant point to address with Plagspotter is that it will not check for duplicate content within a site. It will only check for copied content across other websites, and such is largely a plagiarism checker only.
4. iThenticate
iThenticate is a well-known provider of professional plagiarism tools that are renowned in the academic world as well as online.
Their main goal is to help authors, editors, and researchers ensure their work is unique prior to publication. It has been developed by a company named Turnitin, which is a highly regarded plagiarism checking company for scholars, academics, and educational institutions across the globe.
Along with checking published web pages, it also checks a database of more than 50 million documents and journals. It offers an easy to use service that is cloud-based and provide results quickly.
The only downside to the service, when compared with other duplicate content checkers, is the cost. Although any credits that you buy are valid for 12 months, the minimum credit you can add is $100 which will only cover 1 document of up to 25,000.
If you want to check a website for duplicate content, this is not the best service to use. However, if you have a large text file to check that you wish to publish, they offer an exceptionally thorough service that is second to none.
5. Copyscape
Copyscape is a name that most people will have come across at one time or another. Their plagiarism function is what they are best known for, and they offer a service that is both easy to use and which offers value.
It is particularly good for checking content for external duplication. One of the best features of the Copyscape service is the ability to export information to a CSV file.
They have an additional service called Copy Sentry. This scans the web daily to make sure that your content has not been copied or published online. If it is found, you will receive an instant notification with any related details.
While Copyscape has a solid reputation as a plagiarism checker, it can also help you find internally duplicated content within your own site.
By creating a private index of content, you can easily find out if there is replication on a site. While they do offer this service, their sister company, Siteliner, offers a much easier way to do this.
Copyscape charge 3c per search of up to 200 words, with an additional charge of 1c per every 100 words for their premium service and you need to add a minimum of $10 credit in order to get started.
They offer a free service, a premium service, and their daily update service (Copysentry). If you want to learn more about the copyright laws in your country or how to deal with copyright theft, they also have a huge resources bank of information you can review for free as well.
It is ranked as the best plagiarism software globally and forms part of the Indigo Stream Technologies group.
6. MOZ
In terms of looking for tools that can help detect internally duplicated content, Moz is well-known for this, and a whole lot more. Moz is primarily regarded as a pay-for-functionality SEO tool. However, they do have a range of SEO tools and local marketing tools they offer on their website for free.
You do need to use one of the paid-for MOZ services in order to avail of their internal duplicate content checking feature; this can easily be found and used from the MOZ Crawler function.
If you use the service, you will find that it doesn’t just check for internal duplicate content, it will also search the meta data too.
Any duplicate content will be flagged as a priority, and it is easy to find the location of the duplicate content on your site quickly using this tool.
It also gives you the option of exporting the report which many people like as it makes fixing the issues a little easier.
7. Google Search Console
As you would expect, no other than the king of all search engines had to be featured somewhere on this list.
As well as finding issues with duplicate content, you can also use the Google Search Console to help you detect issues that may be caused by ‘thin content’*.
*Another way people typically refer to thin content is low-quality pages which do not deliver any benefits to the reader. These can include doorway pages, automated content, and page which are duplicated.
There are four key areas you should focus on if you are using the Google Search Console for help with thin or duplicate content.
URL Parameters – Here, Google will let you know if it is encountering any issues with indexing or crawling your website.
This is a quick and easy way to spot URL parameters which lead to duplicate URLs that have been technically created.
Improvements in HTML – Here, Google will detect URLs with title tags and meta descriptions that have been duplicated.
Index Status – Here, Google will display a graph of traffic covering the pages within its historical index. This is particularly useful to review for upward spikes.
If you did not publish any new content to your site, these spikes are indicative of low-quality URLs and duplicate URs which may have made it into the Google Index.
On the spectrum, Google Search Console is a little more technical than the other duplicate content checkers.
However, for those who know how to use it, it can prove to be very telling, and it can help you go straight to the source of the issues with duplicate content.
8. Small SEO Tools
This is purely a plagiarism checker. It is quick and easy to use. The major flaw to this service is the pesky adverts that are scattered across the site. If you can get past this, and you want a no-frills site that checks for copied content, small SEO tools offer just that.
You can upload files from the cloud, choose a file from your Google Drive or Dropbox, and upload either a Docx or text file. Aside from these options, you can quickly copy and paste text into a search box.
9. Duplichecker
This is a tool that specifically checks for plagiarism and enables you to perform DocX, Text, URL, and Text file searches.
It provides unlimited searched for free once you sign up and one free search if you do not wish to register. It will not search within a site for duplicated content, but it will help you to find out if there is any content on your site that is present anywhere else on the web.
How to Fix Duplicate Content Issues
Now that you know the best tools for detecting duplicate and copied content on a website, you can now get started on putting things right.
At this point, it is important to remind you that plagiarizing large amount of content, scraping/duplicated content, and thin content are different.
Copied or Plagiarized Content
The only way to deal with content that is copied from other location on the web is to rewrite and update that content so that it is entirely unique. For many people who may have written their website content some years back, updating the content on a website is always a good thing to do periodically.
However, if the content is not original, then the first task you need to do is hire a professional copywriter to product SEO friendly Copy for you; or to rewrite the content yourself. This is a fix now, fix fast issue.
Content and Copywriter owners can access tools that will search and locate plagiarized content automatically.
So, whether it is images, videos, or words that are copied, you need to ensure that any instances of this are fully removed from your website.
How to Remove Instances of Duplicate Content on a Website
If you copied a post from another website, likely it isn’t THAT big of a deal. The best practice is to canonicalize the content or add attribution. If you do this on a large scale, it could lead to SEO issues.
Creating unique content on your own website is the quickest way to gaining traction in the SERPs, assuming you aren’t writing about content irrelevant to the theme of your site or even relevant content that requires a much stronger website to rank for that content.
Thin Content
Thin content forces the crawlers to figure out which page to rank for the material. Duplicate content scraped from other sites can cause this and even information that is stored on multiple URLs on the same domain. Both of these lead to thin content, high bounce rates, and eventually the loss of positioning in the SERPs.
The key is to keep the content in the “content areas” of the page high quality, long form, original, unique, and ever green. The more you can change out duplicate content that is found on other sites and on other places on your own site, the better your Site optimization will be and more chances you give your site to rank in additional search queries.
If you wonder why you have a 50-page website and google search console is only indexing a few of them, often times, this is the culprit.
Redirect 301
A really effective way to resolve duplicate content issues on a website is by using a 301 redirect. Get rid of those pages all together and 301 redirect that old URL to a name and improved URL.
This is a fully permanent redirection which transmits the link-juice to a different page. When you redirect with a 301, it will not negatively impact your SEO, and you shouldn’t lose any of the traffic which would have come via the old URL.
Sometimes the page with the duplicate content is the better slug. In that case, rework this page and redirect the more original post URL to this one, of course, fix the content on the better slug.
Meta No Index
This method of removing duplicate content is most useful when you have to resolve issues with pages that are being indexed by a search engine. The exact term ‘no index, nofollow’, is input and this enables the robots to know that a specific page should not be getting indexed by a search engine.
You can do this on individual pages or in the /robots.txt file.
Canonical Linking
This is the best way to inform the search engines that a specific page needs to be treated as a copy of a specified page URL that you want to be able to stay live on your site. When scraping others material, use this strategy.
If you need any help finding and correcting duplicate content on your website or you want to find out the best way to boost your SEO, our professional team can help you quickly put things right. With so much of our businesses depending on effective Search Engine Optimization, getting your content written with intent to rank is key.

About The Author:
Elizabeth is a Master of the English language with a relentless passion for research and an eye for detail that surpasses normality.
Having worked within the private sector for many well-known corporations, she gained direct experience within finance, insurance, education, eCommerce, and the IT sector. Communication has always been fundamental to her success in roles that spanned sales, marketing, support, product, business, and channel management.
For the past five years, she has committed herself fully to the role of lead copywriter and researcher; combining a plethora of skills and experience from her past, to deliver word-perfect, well-researched professional content that compels readers and inspires them to take action. Her words make an impact and leave a lasting impression.
Based in the beautiful City of Cambridge, England; Elizabeth is a devoted mum, a life-long F1 enthusiast, and loves to spend time outdoors.
