Google Ads is one of the most popular digital advertising platforms available today. Businesses and marketers use it to reach potential customers across Google’s extensive network, which includes its search engine, partner websites, and YouTube. But one of the most common questions asked by those new to the platform is, “How much do Google Ads cost?”
In this article, we’ll break down the costs associated with Google Ads, delve into the factors that influence these costs, and explore why the prices vary from industry to industry and campaign to campaign.
The Basics: Pay-Per-Click (PPC)
Google Ads primarily operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model. This means that you are charged each time someone clicks on your ad. Sounds simple, right? While the basic premise is straightforward, the reality is far more complex.
Average Costs
According to industry estimates, the average cost-per-click (CPC) on Google Ads can range from $1 to $2 for the Search Network and less than $1 for the Display Network. Remember that these are averages. The actual costs can vary widely depending on several factors, such as industry, keywords, and competition.
Factors Affecting Costs
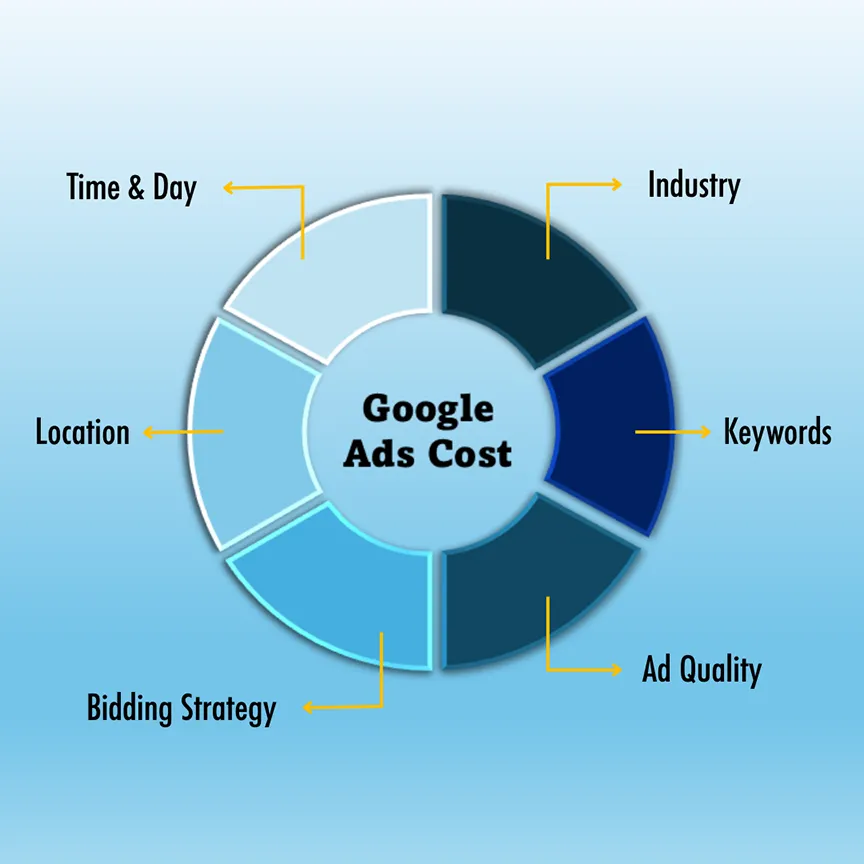
1. Industry
The industry you are in significantly impacts the CPC. Highly competitive industries like legal services and insurance often have higher CPCs. On the other hand, less competitive sectors like arts and crafts may have much lower CPCs. Hotel ads are also calculated differently than other industries.
2. Keywords
Keywords are the search terms you want to target. Some keywords are competitive because many businesses are trying to rank for them. Competitive keywords are generally more expensive.
3. Ad Quality
Google rates ads using its Quality Score to evaluate the relevance and quality of your ads and landing pages. This is a numerical score between 1-10. A higher Quality Score can lead to lower costs and better ad placements.
4. Geographical Location
The cost can also vary depending on the geographical location you are targeting. For example, targeting an audience in New York may be more expensive than targeting an audience in a rural area.
5. Time and Day
The time and day you run your ads can impact costs. Costs can rise during peak business hours and drop during off-hours. Running an ad at midnight won’t get as many clicks or views, but it can save money.
6. Bidding Strategy
Google Ads offers several bidding strategies. These include manual bidding, automated bidding, and portfolio bidding. Each has its own pros and cons, affecting both the costs and the outcomes of your campaigns. This is something you should research or discuss with your marketing agency.
Why Do Costs Vary?
There are a number of factors that go into calculating costs and modifying them. Here are a few of the factors that you need to keep in mind when doing your calculations:
Competition
The number one reason for cost variation is competition. The Google Ads platform functions like an auction where advertisers bid for keywords. The more advertisers there are bidding for the same keywords, the higher the cost.
Consumer Behavior
Seasonal trends, market demands, and consumer behavior can also contribute to cost fluctuations. Umbrella sellers may see a spike in CPC during the rainy season due to increased demand. During drier seasons, they may see the cost of their ad campaign plummet.
Algorithm Updates
Google frequently updates its algorithms, affecting ad placements and, consequently, costs. Staying updated on these changes can help you manage costs better. Staying informed on any changes is also a great way to remain more flexible to market changes.
How to Control Costs

With an array of variables influencing the price you pay for each click, mastering the art of cost-efficiency becomes vital for maximizing returns on your marketing investments. Let’s take a look at the various techniques and strategies you can employ to control Google ad costs while running campaigns.
Set a Well-Defined Budget
The first step in controlling costs is to establish a realistic budget for your campaign. Google Ads offers you the flexibility to set daily budgets, giving you a granular level of control. By knowing how much you’re willing to spend each day, you can avoid unexpected expenses and better plan your overall marketing strategy.
Make sure your budget aligns with your business goals. If you are spending too little, it can result in low visibility, while overspending can eat into your ROI. The budget will also help you reduce the shock of sudden bursts of interest or clicks.
Understand Bidding Strategies
Google Ads offers multiple bidding strategies, each with its own set of rules and benefits. Here are some popular options:
- Manual CPC Bidding: You set the maximum amount you’re willing to pay for a click. This gives you control but requires constant monitoring to adjust bids based on performance.
- Automated Bidding: Google’s algorithms set the bid based on the likelihood of your ad achieving the set objective. While convenient, you relinquish some control over costs.
- Enhanced CPC (ECPC): A middle-ground option where Google adjusts your manual bids to help you get more conversions.
- CPA Bidding: You set a target cost-per-acquisition (CPA), and Google sets the bids to get as many conversions at that target CPA.
Understanding the nuances of each strategy can help you pick the one that works with both your objectives and budget constraints.
Use Negative Keywords
One of the most effective ways to control costs is by using negative keywords. These are terms that will prevent your ad from showing. By setting negative keywords, you prevent your ads from triggering irrelevant or low-converting searches. Having a strong focus on your target customer group can save money on useless clicks.
Leverage Ad Scheduling
Google Ads allows you to schedule your ads to appear on specific days and times. By analyzing the performance metrics of your campaign, you can identify peak times for user engagement and focus your advertising efforts during those hours.
This strategy is often referred to as “dayparting.” It can reduce costs by eliminating low-performing hours from your ad schedule.
Monitor Quality Score
Quality Score is Google’s rating of the quality and relevance of your keywords and PPC ads. A higher Quality Score can lead to lower costs and better ad positions. It is determined by:
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): The percentage of clicks to impressions.
- Ad Relevance: How closely the ad matches the intent behind the keyword.
- Landing Page Experience: The quality of the web page where users land after clicking the ad.
Improving any of these factors can positively impact your Quality Score, which could reduce your CPC.
Use Geo-Targeting
If your business serves specific locations, there’s no point in displaying your ads worldwide. Geo-targeting allows you to show your ads only in the geographic locations that are relevant to your business.
Not only does this reduce wasted clicks from halfway around the world, but it also helps you reach your desired demographic. There will be less competition in a geo-located area for clicks and attention.
Conduct A/B Testing
Regularly test different elements of your ads and landing pages to identify what’s working and what’s not. A/B testing can involve changing headlines, ad copy, images, or calls to action (CTA). By continually refining your ads, you can improve their performance and your return on investment.
A/B testing will also help you refine your target customer. What that means is that you are maximizing advertising investment while also improving effectiveness.
Analyze and Adjust
One of the most effective ways to control costs is by continually analyzing the performance of your campaigns. Google Ads provides a wealth of data that you can use to understand what’s working and what’s not.
Regularly monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) like CPC, CTR, and CPA can provide insights into where you might be overspending or underutilizing your budget.
Control Costs to Succeed
Controlling costs in Google Ads is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process that requires strategic planning, continuous monitoring, and timely adjustments. Setting a realistic budget and choosing the appropriate bidding strategy is vital.
Also, there are leveraging features like negative keywords, ad scheduling, and Quality Score optimization. There are multiple options for you to keep your ad spend in check.
By combining these strategies, not only can you control Google Ad costs, but you can also improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your advertising campaigns. The ultimate goal isn’t as simple as to just spend less. The best outcome is to spend smarter, maximizing the return on every dollar invested in your Google Ads campaigns.
