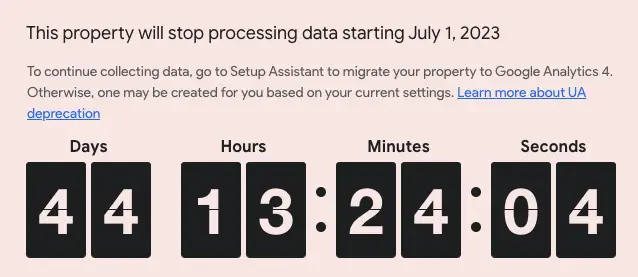
Google Analytics (GA) has been a go-to tool for businesses of all sizes looking to gain insights into their website traffic and user behavior. Over the years, Google has made a number of updates to the platform, with the most recent being the transition from Universal Analytics (UA) to Google Analytics 4 (GA4). This transition is mandatory, and businesses need to be aware of the key differences between the two platforms and what they need to do to prepare for the switch.
Differences Between GA4 and UA
The biggest difference between GA4 and UA is the way that they track and process data. UA relies on cookies to track user behavior across multiple sessions and devices. However, with privacy concerns on the rise, this method of tracking is becoming less effective. GA4 uses an event-driven data model that relies on Google’s machine-learning algorithms to analyze user behavior and provide insights.
Another key difference is the way that data is organized and reported. In UA, data is organized into hits, sessions, and users. In GA4, data is organized into events, user properties, and app and web data streams. This new approach allows for more granular tracking of user behavior and provides more detailed insights into how users interact with a website or app.
Additionally, GA4 offers a number of new features that are not available in UA. For example, GA4 includes enhanced measurement capabilities, such as automatic event tracking, scroll tracking, and outbound link tracking. It also offers improved cross-device tracking and the ability to track app and web interactions in a single property.
Preparing for the Transition
As mentioned earlier, the transition from UA to GA4 is mandatory, so businesses need to prepare for the switch. Here are some key steps to take to ensure a smooth transition:
Create a New GA4 Property
Businesses need to create a new GA4 property alongside their existing UA property. This will ensure that they continue to collect data during the transition period.
Set Up Data Streams
GA4 allows for the tracking of both app and web data in a single property. Businesses need to set up data streams to ensure that they are collecting data from both sources.
Adjust Website Tracking
With the event-driven model of GA4, businesses need to adjust their website tracking to ensure that they are capturing the right events and user properties.
Review and Update Tracking Tags
Businesses need to review their tracking tags to ensure that they are compatible with GA4. If they are not, they need to update their tags accordingly.
Familiarize Yourself with the New Reporting Interface
GA4 has a new reporting interface that is different from UA. Businesses need to familiarize themselves with this new interface to ensure that they can effectively analyze their data.
Take Advantage of It
The transition from UA to GA4 is an important change that businesses need to be aware of. While there are some key differences between the two platforms, GA4 offers a number of new features that can help businesses gain deeper insights into their website traffic and user behavior.
To prepare for the transition, businesses need to take a number of key steps, including creating a new GA4 property, setting up data streams, adjusting website tracking, reviewing and updating tracking tags, and familiarizing themselves with the new reporting interface. By taking these steps, businesses can ensure a seamless transition to GA4 and continue to gain valuable insights into their online presence.
